Detecting cancer at an early stage means to identify the cancer before it produces symptoms. This can be challenging as cancer in its initial stages manifests in subtle symptoms which are missed or ignored. Some symptoms which may require further examination to rule out cancer are:
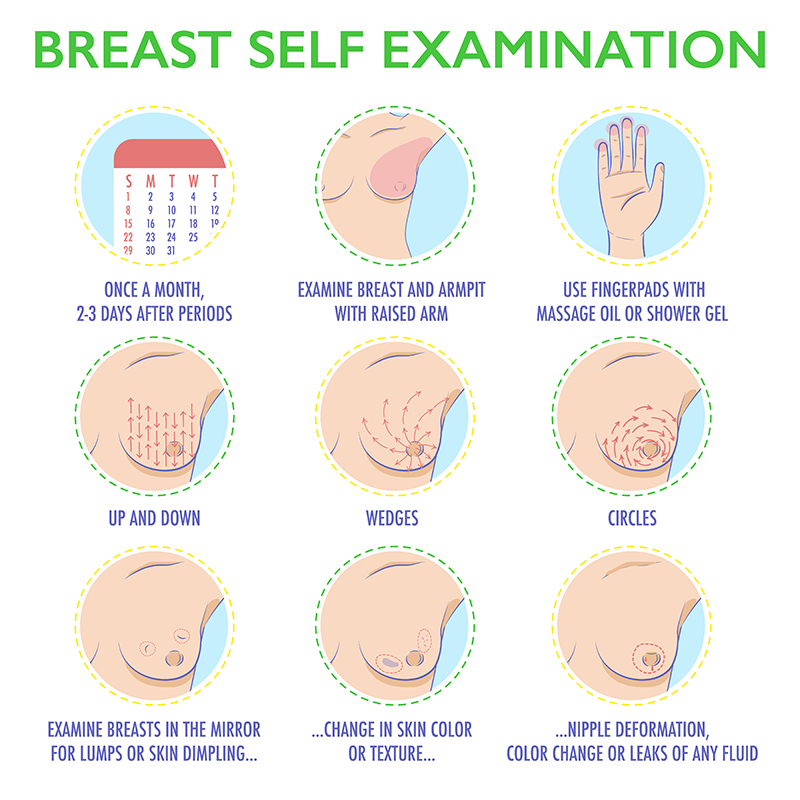
| Age |
The proposed age to begin screening for breast cancer is 25 years. Women should know how their normal breast looks and should report if there is any variance in size, color, contours or shape. From the age of 40 women are advised to undergo a mammogram annually. |
|---|---|
| Tests |
|
| Types |
In situ (Non- invasive) Breast Cancer - which have not spread
Invasive (Infiltrating) Breast Cancer - which have spread
|
| Side Effects |
pain at incision site after breast biopsy / over diagnosis |
The proposed age to begin screening for breast cancer is 25 years. Women should know how their normal breast looks and should report if there is any variance in size, color, contours or shape. From the age of 40 women are advised to undergo a mammogram annually.
In situ (Non- invasive) Breast Cancer - which have not spread
Invasive (Infiltrating) Breast Cancer - which have spread
pain at incision site after breast biopsy / over diagnosis
| Age |
|
|---|---|
| Tests |
Stool based tests
Visual Tests
|
| Types |
|
| Side Effects |
|
Stool based tests
Visual Tests
| Age |
yearly low dose CT scans are advised from 55 years onwards people who are in fairly good health and have smoked or quit smoking in the past 15 years. |
|---|---|
| Tests |
|
| Types |
|
| Side Effects |
There are usually no side effects after any of the scans and x rays. During a bronchoscopy examination, the patient is usually sedated. there may be some pain, discomfort and drowsiness after the test is done. |
yearly low dose CT scans are advised from 55 years onwards people who are in fairly good health and have smoked or quit smoking in the past 15 years.
There are usually no side effects after any of the scans and x rays. During a bronchoscopy examination, the patient is usually sedated. there may be some pain, discomfort and drowsiness after the test is done.
| Age |
Men in the age group of 50 years are at high risk of getting prostate cancer especially if they have a history of a first degree relative who has had prostate cancer at an early age. |
|---|---|
| Tests |
|
| Types |
Adenocarcinoma: cancer which develops from the gland cells |
| Side Effects |
There may be slight discomfort after digital rectal examination Pain may be experienced after TRUS guided biopsy and fine needle biopsy |
Men in the age group of 50 years are at high risk of getting prostate cancer especially if they have a history of a first degree relative who has had prostate cancer at an early age.
Adenocarcinoma: cancer which develops from the gland cells
There may be slight discomfort after digital rectal examination Pain may be experienced after TRUS guided biopsy and fine needle biopsy
| Age |
Women should start cervical cancer screenings by getting a Pap test at 21. The test should be taken every 3 years until 30. From 30 onwards, an HPV test should be taken along with the Pap test as well. |
|---|---|
| Tests |
|
| Types |
|
| Side Effects |
|
Women should start cervical cancer screenings by getting a Pap test at 21. The test should be taken every 3 years until 30. From 30 onwards, an HPV test should be taken along with the Pap test as well.
| Age |
For those who have a history of tobacco chewing or smoking must get a regular check of the oral cavity done. |
|---|---|
| Tests |
|
| Types |
|
| Side Effects |
Only incisional or FNAC biopsies may be painful. Other tests are non invasive and do not hurt. |
For those who have a history of tobacco chewing or smoking must get a regular check of the oral cavity done.
Only incisional or FNAC biopsies may be painful. Other tests are non invasive and do not hurt.
Benefits of Screening Tests